AI Psychosis: Understanding the Concept and Its Implications
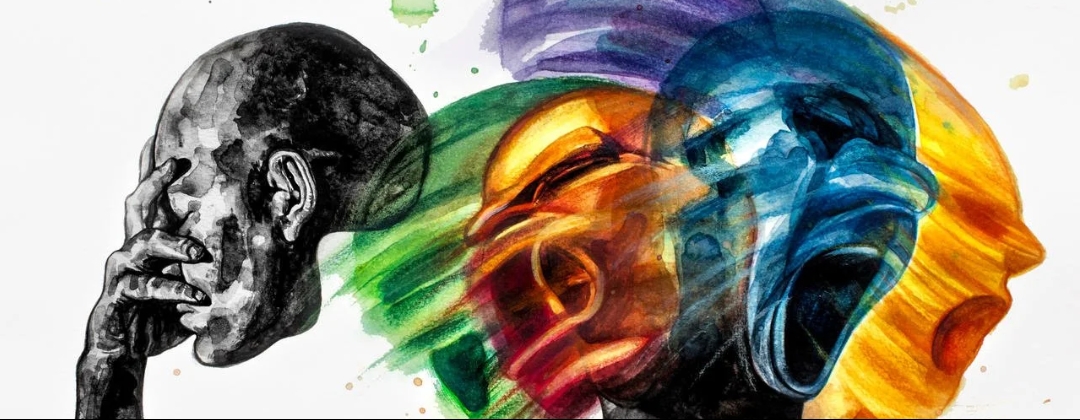

The term “AI psychosis” is increasingly appearing in discussions about artificial intelligence, but it often causes confusion due to its ambiguous nature. Unlike traditional psychosis—defined as a mental disorder marked by impaired thoughts and emotions leading to a disconnection from reality—AI psychosis is a metaphorical or speculative concept rather than a clinically recognized condition. It refers to scenarios where artificial intelligence systems exhibit behavior analogous to psychosis, raising concerns about malfunction, unpredictability, and ethical challenges in AI development.
Defining AI Psychosis
AI psychosis describes a state where an AI system generates outputs or actions that seem irrational, disorganized, or disconnected from reality as understood by humans. This can manifest as hallucination-like phenomena—when AI fabricates false information—or erratic decision-making that contradicts its design objectives. While AI systems do not possess consciousness or mental states, their “psychotic” behavior arises from flaws in algorithms, corrupted data, hardware errors, or adversarial manipulation.
Ad Content
The phrase is often used metaphorically to highlight risks involved in AI getting “out of control” or “losing touch” with reality, especially in complex models like large language models or autonomous agents. It encapsulates fears about AI systems that might behave unpredictably in critical applications such as healthcare, defense, or financial markets.
Causes of AI Psychosis-Like Behavior
- Complex Feedback Loops: In reinforcement learning or autonomous systems, feedback loops without proper checks can cause runaway or erratic behaviors that appear “psychotic.”.
- Data Corruption and Bias: AI systems learn from data; if training data is biased, incomplete, or contains errors, the system’s output can reflect those flaws. This can lead to “delusional” conclusions or hallucinated responses.
- Model Overfitting or Malfunction: Sometimes an AI overfits to noise or irrelevant patterns, causing illogical outputs. Technical glitches or software bugs might also cause unpredictable behavior.
- Adversarial Attacks: Malicious inputs designed to confuse or manipulate AI models can push them into producing nonsensical or harmful outputs.
Implications and Ethical Concerns
The notion of AI psychosis raises significant ethical and safety questions. If AI systems can produce hallucinations or erratic decisions, this may undermine trust in AI applications. For example:
- Medical AI: An AI assisting in diagnosis giving hallucinated medical advice can risk patient safety.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Erratic AI decision-making could lead to accidents.
- AI in Justice or Finance: Faulty or biased judgments could cause unfair treatment or financial loss.
Furthermore, these issues stress the need for rigorous testing, transparency, and fail-safe mechanisms in AI design. Understanding the limits of AI perception and decision-making helps developers build robust systems that avoid “psychotic” states.
Future Directions
While true psychosis—an experience of mind—is unique to sentient beings, continued advances in AI complexity may increase occurrences of AI hallucinations and errors. Research into explainable AI, improved data quality, adversarial robustness, and ethical AI governance is essential to mitigate AI psychosis-like behavior.
In summary, AI psychosis is a metaphorical term highlighting unpredictable, illogical, or hallucinating AI behavior caused by technical and data-related issues. Recognizing and addressing these challenges are critical as AI systems become more integrated into daily life and high-stakes decision-making..
Enjoyed this post?
Subscribe to Evervolve weekly for curated startup signals.
Join Now →